

Diaphragm Constraint
Dynamic Analysis
Grid Lines
Mesh Areas
Mode Shapes
New Model From Template
Linear Replication
Response Spectrum Analysis
Click the File menu > New Model command to access the New Model form.
Click the drop-down list in the status bar to change the units to ![]() .
.
Click on the 3D Frames button  to access the 3D Frames form. In that form:
to access the 3D Frames form. In that form:
Select Open Frame Building from the 3D Frame Type drop-down list.
Type 4 in the Number of Stories edit box.
Type 4 in the Number of Bays, X edit box.
Type 4 in the Number of Bays, Y edit box.
Accept the default Story Height, 144.
Type 30 ft (be sure to type the ft) in the Bay width, X edit box.
Type 30 ft (be sure to type the ft) in the Bay width, Y edit box.
Click the + (plus) symbol beside the Beams or Columns drop-down list to access the Frame Properties form.
Click the Import New Property button to access the Import Frame Section Property form.
Select Steel in the Frame Section Property Type drop-down list.
Click the Pipe button to access the Section Property File form.
Select the SECTIONS.PRO file and click the Open button to access a database form listing the available sections.
Click the + (plus) symbol beside the Material drop-down list to access the Define Materials form.
Click the Add New Material Quick button to access the Quick Material Definition form.
Select Steel in the Material Type drop-down list.
Select ASTM A53 Grade B in the Specifications drop-down list.
Click the OK button to close the Quick Material Definition form and return to the Define Materials form.
Highlight the A53GrB definition in the Materials display list and click the Modify/Show Material button to access the Material Property Data form.
Change the Units to ![]() .
.
Verify that the Weight per unit Volume is 0.49.
Verify that the Units are set to ![]() .
.
Verify that the Modulus of Elasticity is 29000.
Verify that Poisson’s ratio is 0.3.
Click the OK buttons on the Material Property Data and Define Materials forms to close those forms and return to the database form.
Ensure that the A53GrB definition is selected in the Materials drop-down list.
Click on the P3 section and then the OK button to access the Pipe Section form.
Click the OK button on the Pipe Section form to return to the Frame Properties form.
Click the Add New Property button to access the Add Frame Section Property form.
Select Concrete in the Frame Section Property Type drop-down list.
Click the Rectangular button to access the Rectangular Section form.
Type BMCOL in the Section Name edit box.
Click the + (plus) symbol beside the Material drop-down list to access the Define Materials form.
Highlight the 4000Psi definition in the Materials display list and click the Modify/Show Material button to access the Material Property Data form.
Change the Units to ![]() .
.
Verify that the Weight per unit Volume is 0.15.
Change the Units to ![]()
Type 3600 in the Modulus of Elasticity edit box .
Verify that the Poisson’s ratio is 0.2.
Click the OK buttons to close the Material Property Data and the Define Materials forms and return to the Rectangular Section form.
Type 20 in the Depth (t3) edit box.
Type 20 in the Width (t2) edit box.
Click the OK buttons on the Rectangular Section and Frame Properties forms to exit those forms and return to the 3D Frames form.
Select the BMCOL definition in the Beams and Columns drop-down lists.
Verify that the Restraints check box is checked.
Click the OK button to close the 3D Frames form and display the model template in the program windows.
Click the Define menu > Section Properties > Area Sections command to access the Area Sections form.
In the Select Section Type to Add drop-down list, select the Shell option.
Click the Add New Section button to access the Shell Section Data form. In that form:
Type WALL in the Section Name edit box.
In the Type area, verify that the Shell-Thin option is selected.
Verify that the 4000Psi definition is selected in the Material Name drop-down list.
Type 12 in the Membrane edit box.
Type 12 in the Bending edit box.
Click the OK button to return to the Area Sections form.
Click the Add New Section button to access the Shell Section Data form.
Type FLOOR in the Section Name edit box.
Verify that the 4000Psi definition is selected in the Material Name drop-down list.
Type 10 in the Membrane edit box.
Type 10 in the Bending edit box.
Click the OK buttons on the Shell Section Data and Area Sections forms to exit all forms.
Click the drop-down box in the status bar to change the units to ![]() .
.
Click the Define menu > Coordinate Systems/Grids command to access the Coordinate/Grid Systems form. In that form:
Click the Modify/Show System button to access the Define Grid System Data form. In that form:
Verify that the Ordinates option is selected in the Display Grids as area in the middle right of the form.
Check the Glue to Grid Lines check box.
In the X Grid Data portion of the spreadsheet, click the -30 in the row 2 Ordinate cell and type -35 in that cell. Click on the 30 in the row 4 Ordinate cell and type 40 in that cell.
In the Y Grid Data portion of the spreadsheet, click on the -30 in the row 2 Ordinate cell and type -40 in that cell.
Click the OK buttons on the Define Grid System Data and Coordinate/Grid Systems forms to exit all forms.
Verify that the 3-D View window is active. The window is active when its title is highlighted.
Click the Set Display Options button to access the Display Options for Active Window form. In that form:
Check the Fill Objects check box.
Click the OK button.
Click in the window labeled X-Y Plane @ Z=48 to activate it. If necessary, use the Move Up/Down in List buttons ![]() to change to Z=48.
to change to Z=48.
Click the Set Display Options button to access the Display Options for Active Window form. In that form:
Check the Fill Objects check box.
Click the OK button.
Click the XZ View button ![]() . The view switches to the X-Z plane @ Y=60 and appears as shown in Figure Z-1.
. The view switches to the X-Z plane @ Y=60 and appears as shown in Figure Z-1.

Figure Z-1: Screen After Step 11
Click the Quick Draw Area Element button ![]() to display the Properties of Object form.
to display the Properties of Object form.
Select Wall in the Section drop-down list.
Click once in each of the regions labeled “A,” “B,” “C” and “D” in Figure Z-1 to enter four area objects.
Click the View menu > Set 2D View command to display the Set 2D View form. In that form:
Select the X-Z Plane option.
Type -60 in the Y= edit box.
Click the OK button. The screen appears similar to that shown in Figure Z-1 (except that the location is now at Y=-60).
Click once in each of the regions labeled “E,” “F,” “G” and “H” in Figure Z-1 to enter four area objects.
Click the View menu > Set 2D View command to display the Set 2D View form. In that form:
Select the Y-Z Plane option.
Type 60 in the X= edit box.
Click the OK button. The screen appears as shown in Figure Z-2
.
Figure Z-2: Screen After Step 16
Click once in each of the regions labeled “A,” “B,” “C” and “D” in Figure Z-2 to enter four area objects.
Click the View menu > Set 2D View command to access the Set 2D View form.
In that form:
Select the Y-Z Plane option.
Type -60 in the X= edit box.
Click the OK button. The screen appears similar to that shown in Figure Z-2 (except that the location is now at X=-60).
Click once in each of the regions labeled “E,” “F,” “G” and “H” in Figure Z-2 to enter four area objects. This completes the drawing of the shear walls.
Click in the window labeled Y-Z Plane @ X=-60 to verify it is active.
Click the View menu > Set 2D View command to access the Set 2D View form. In that form:
Select the X-Y Plane option.
Type 48 in the Z= edit box.
Click the OK button.
Click the Set Display Options button ![]() (or the View menu > Set Display Options command) to access the Display Options for Active Window form. In that form:
(or the View menu > Set Display Options command) to access the Display Options for Active Window form. In that form:
Check the Labels box in the Joints area.
Click the OK button.
Click the Draw Rectangular Area button ![]() or the Draw menu > Draw Rectangular Area command to access the Properties of Object form. In that form:
or the Draw menu > Draw Rectangular Area command to access the Properties of Object form. In that form:
Verify that FLOOR is shown in the Section drop-down list.
Click on joint 25 and then joint 105 to enter a single area object for the entire floor.
Click the Set Select Mode button ![]() to exit Draw mode and enter Select mode.
to exit Draw mode and enter Select mode.
Select all objects in the X-Y Plane @ Z=48 by “windowing.”
Click the Edit menu > Edit Areas > Divide Areas command to access the Divide Selected Areas form. In that form:
Select the Divide Area Based On Points On Area Edges option and check the Selected Point Objects on Area Edges check box.
Click the OK button.
Select all objects in the X-Y Plane @ Z=48 by “windowing.”
Click the Edit menu > Replicate command to access the Replicate form. In that form:
Verify the Linear Tab is selected.
In the Distance area type -12 in the dz edit box.
Verify that 0 is entered in the dx and dy edit boxes.
Type 3 in the Number edit box.
Click the OK button to proceed with the replication and create the other floor diaphragms.
Click the Select All button ![]() .
.
Click the Assign menu > Joint > Constraints command to access the Assign/Define Constraints form. In that form:
In the Choose Constraint Type for Add area click the drop-down list and select Diaphragm.
Click the Add New Constraint button to access the Diaphragm Constraint form. In that form:
Type DIAPH in the Constraint Name edit box.
Select the Z Axis option in the Constraint Axis area.
Check the Assign a different diaphragm constraint to each different selected Z level box. This will assign a diaphragm constraint at each floor level with the different diaphragms identified by their respective elevations.
Click the OK buttons on the Diaphragm Constraint and Assign/Define Constraints forms to exit all forms.
Click the View menu > Set 2D View command to access the Set 2D View form. In that form:
Select the X-Y Plane option.
Verify that 0 is entered in the Z= edit box.
Click the OK button.
Select all objects at this level by “windowing.”
Click the Assign menu > Joint > Restraints command to access the Joint Restraints form. In that form:
Click the Fixed Support button ![]() in the Fast Restraints area.
in the Fast Restraints area.
Click the OK button.
Click the View menu > Set 2D View command to access the Set 2D View form. In that form:
Select the X-Z Plane option.
Type -60 in the Y= edit box.
Click the OK button.
Click the Define menu > Coordinate Systems/Grids command to access the Coordinate/Grid Systems form. In that form:
Click the Modify/Show System button to access the Define Grid System Data form. In that form:
Verify that the Ordinates option is selected in the Display Grids as area in the middle right of the form.
In the Z Grid Data portion of the spreadsheet, type z6 in the Grid ID cell of row 6. In that same row, type 78 in the Ordinate cell and click in the Line Type cell to display Primary, the Visibility cell to display Show, and Bubble Loc. cell to display End.
Click the OK buttons on the Define Grid System Data and Coordinate/Grid Systems forms to exit all forms.
Click the View menu > Set 2D View command to access the Set 2D View form. In that form:
Select the X-Z Plane option.
Type -60 in the Y= edit box.
Click the OK button. The screen appears as shown in Figure Z-3.
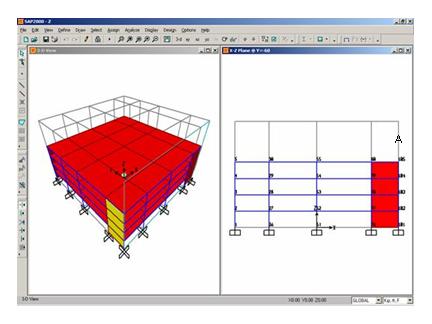
Figure Z-3: Screen After Step 46
Click the Quick Draw Frame/Cable Element button ![]() or the Draw menu > Quick Draw Frame/Cable/Tendon command to access the Properties of Object form. In that form:
or the Draw menu > Quick Draw Frame/Cable/Tendon command to access the Properties of Object form. In that form:
Select P3 from the Section drop-down list.
Verify that Continuous is shown in the Moment Releases drop-down list.
Click on the grid line at the point labeled “A” in Figure Z-3 to enter the flagpole frame object.
Click the Set Select Mode button ![]() to exit Draw mode and enter Select mode.
to exit Draw mode and enter Select mode.
Click the drop-down list in the status bar to change the units to ![]() .
.
Click on the joint at the top of the flagpole to select it.
Click the Assign menu > Joint > Masses command to access the Joint Masses form. In that form:
Type .00065 in the Direction 1, Direction 2 and Direction 3 edit boxes.
Click the OK button.
Click the Show Undeformed Shape button ![]() to remove the displayed joint mass assignments.
to remove the displayed joint mass assignments.
Click the drop-down list in the status bar to change the units to ![]() .
.
Click the Define menu > Functions > Response Spectrum command to access the Define Response Spectrum Functions form. In that form:
In the Choose Function Type to Add area, click the drop-down list and select UBC 94 Spectrum.
Click the Add New Function button to access the Response Spectrum UBC 94 Function Definition form. In that form:
Type SPEC1 in the Function Name edit box.
In the Parameters area, select 2 from the Soil Type drop-down list.
Click the OK buttons on the Response Spectrum UBC 94 Function Definition and Define Response Spectrum Functions forms to exit all forms.
Click the Define menu > Load Cases command to access the Define Load Cases form. In that form:
Click the Add New Load Case button to access the Load Case Data – Linear Static form. In that form:
Type RS1 in the Load Case Name edit box.
In the Analysis Case Type area, select Response Spectrum from the drop-down list.
Accept the default Modal Combination option, CQC.
Accept the default Directional Combination option, SRSS.
In the Loads Applied area:
Verify that U1 is shown in the Load Name drop-down list.
Verify that SPEC1 is shown in the Function drop-down list.
Type 32.2 in the Scale Factor edit box.
Click the Add button.
In the Loads Applied area:
Select U2 in the Load Name drop-down list.
Verify that SPEC1 is shown in the Function drop-down list.
Type 9.66 (.3*32.2=9.66) in the Scale Factor edit box.
Click the Add button.
Verify that Modal Damping is set to Constant at 0.05.
Click the OK button.
Click on MODAL in the Case Name list to highlight it.
Click the Modify/Show Case button to access the Load Case Data - Modal form. In that form:
Select the Ritz Vectors option in the Type of Modes area.
In the Number of Modes area, type 20 in the Maximum Number of Modes edit box.
Select Accel from the Load Type drop-down list in the Loads Applied area.
Verify that UX is shown in the Load Name drop-down list.
Click on the Add button.
Select UY from the Load Name drop-down list.
Click on the Add button.
Click the OK buttons on the Load Case Data – Modal and Define Load Cases forms to exit all forms.
Click the Run Analysis button ![]() to access the Set Load Cases to Run form. In that form:
to access the Set Load Cases to Run form. In that form:
Click the Run Now button.
When the analysis is complete, check the messages in the SAP Analysis Monitor window (there should be no warnings or errors) and then click the OK button to close the window.
Click in the window with the elevation showing to make sure it is active.
Click the View menu > Set 2D View command to access the Set 2D View form. In that form:
Select the X-Z Plane option.
Type -60 in the Y= edit box.
Click the OK button.
Click the Display menu > Show Deformed Shape command to access the Deformed Shape form. In that form:
Select RS1 from the Case/Combo Name drop-down list.
Click the OK button.
Right click the joints at the top and bottom of the flagpole to see their displacements.
Note: If the top of the flagpole goes off of the screen when the deformed shape is displayed, click the Zoom Out One Step button ![]() as many times as required to bring the joint back on to the screen.
as many times as required to bring the joint back on to the screen.